Spread strategies and spread trades are commonly used in trading futures to manage risk and capitalize on price differences between related contracts. Without cross pair trading in crypto space would not become very popular as few markets would exist.
At some point, stablecoins emerged which brought more transition way of trading with having pair like BTC/USDT, ETH/USDT. When executing spread trades, a simultaneous purchase and sale of related futures contracts is a key aspect, allowing traders to take advantage of price differentials while managing risk.
Understanding the key concepts of futures spread trading—such as market mechanics, risk management, and the importance of quick execution—is essential for success in this area.
Introduction to Crypto Arbitrage
Crypto arbitrage is a trading approach that seeks to profit from price differences between two or more markets. In the world of spread trading, this means taking advantage of discrepancies in the prices of cryptocurrency futures contracts across different exchanges or contract months. By simultaneously buying and selling futures contracts where a price difference exists, traders can lock in a profit regardless of the overall market direction.
For example, if a futures contract for Bitcoin is trading at a lower price on one exchange and higher on another, a trader can buy the cheaper contract and sell the more expensive one at the same time. This spread trading strategy allows traders to benefit from the price difference between the two contracts, rather than relying on the absolute price movement of the underlying asset.
Crypto arbitrage using futures spread trading requires a solid understanding of how futures contracts work, as well as the ability to quickly execute trades and manage risk. Since price differences can be fleeting, successful arbitrage depends on speed, precision, and effective risk management. By focusing on the price difference between contracts, rather than outright market direction, traders can reduce their exposure to volatility and potentially achieve more consistent returns in the fast-moving crypto markets.
Disadvantage of Cross Trading
You could sell only what you have. So when a Bitcoin is falling, you should sell it. With a limited number of options, you can sell it against ETH or other cryptos. But if all is falling you should sell it against fiat currency or stablecoin if any. So, back in times without stablecoins, traders either had to accept loss or take crypto out of the exchange and sell it at a broker.
Cross Pairs Give Flexibility
Large numbers of cross pairs that were available at Binance, Bittrex or HitBTC offered a very flexible approach by trading cross pairs to almost anything on the spot market. However, with futures trading, cross pairs are not available as a product. Though crypto could be the first market to show such synthetic products.
If you need to understand what are futures and what are the benefits of trading crypto futures please refer to our in-depth guide on Bitcoin Futures Trading.
Understanding Futures Contracts
Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell a specific underlying asset at a predetermined price on a set future date. These contracts are traded on exchanges and are widely used by traders to speculate on price movements or to hedge against potential losses in the market. Futures contracts can be based on a variety of assets, including commodities, currencies, and financial instruments.
In spread trading, traders buy and sell two or more futures contracts—often with different expiration dates or underlying assets—to create a futures spread. The goal is to profit from the price difference between these contracts, rather than from the outright price movement of a single futures contract.
Key characteristics of futures contracts that impact spread trading strategies include:
-
Expiration Date: The specific date when the futures contract expires and must be settled.
-
Underlying Asset: The asset on which the contract is based, such as Bitcoin, corn, or crude oil.
-
Contract Size: The quantity of the underlying asset represented by one futures contract.
-
Tick Size: The minimum price increment by which the contract can move.
-
Margin Requirements: The amount of capital required to open and maintain a futures position.
These features are crucial for spread traders, as they determine how futures contracts are traded, the level of risk involved, and the potential for profit from price movements. Understanding these elements helps traders develop effective spread trading strategies, manage risk, and take advantage of trading opportunities in the futures markets. By focusing on the price difference between contracts, spread traders can navigate the complexities of the futures market with greater confidence and control.
Example of Futures Spread
A typical example of calendar spreads in futures trading is trading two contracts of futures on oil. This is specifically known as an intra commodity calendar spread, where both contracts are for the same commodity but with different contract months. For example, a futures contract with Apr-21 and May-21 expiration dates. Going long (buy) the contract with the Apr-21 contract month while going short (sell) on the May-21 contract month will give us a spread. In this intra commodity calendar spread, traders may use a shorter dated contract, such as Apr-21, and a December contract to take advantage of seasonal price movements. The nearest available futures contract is also known as an outright futures contract.
Popular assets of futures spreads are commodity futures and fixed income securities, like bonds. Any futures products are suitable to create a futures spread. Trading strategy using commodities could also include different classes, like wheat futures, corn futures, or soybean futures to create a spread trade, but intra commodity calendar spreads focus on contracts of the same commodity with different expiration dates.
Real-life example. A conflict in the Middle East hits the news. This is a potential risk for short term shortages in delivery of crude oil. It will likely affect the outright contract for Oil (closest trading contract). Further expiration contracts will also be affected as we are not sure what will happen, but there is a high probability that the conflict will be solved in a few months’ time. Thus, the effect on further expiration contracts will be lower. So the more distant we are from the contract the less volatility will be in that product. We can assume that Apr-21 will be more affected than May-21.
If our stake was at the growth of the Oil, then Apr-21 will be more affected than May-21. Gain on Apr-21 will be larger than the loss on May-21. This is an example of a bull futures strategy within calendar spreads, where the trader expects prices to rise and positions accordingly.
So trading a futures spread will make a synthetic product that has smaller volatility. Each one leg of the spread represents a separate futures position, and the spread acts as a risk mitigation tool, often allowing for lower margin requirements. It should be noted that spread trading is a kind of arbitrage strategies.
Types of Futures Spreads
Spreads involve various strategies, including intermarket spreads, intramarket spreads, inter commodity spread, and commodity product spreads, each designed to capitalize on different market relationships and opportunities.
There are two types of futures spreads in crypto trading.
First, you can create a spread on different cryptocurrencies, which can be considered intermarket spreads or, in traditional markets, spreads between closely related commodities. These strategies are similar to trading spreads between related commodities like gold and silver or corn and soybeans, where understanding the market relationship and the dynamics of related markets is crucial for identifying trading opportunities and managing risk. Example: ETH/BTC
Second, you can trade the same product with different maturity, known as intramarket spreads. This is similar to the example we’ve covered above. Example: BTC-0321/BTC-0621.
In traditional commodity markets, inter commodity futures and commodity product spreads involve trading related commodities or a commodity product and its derivative, such as a wheat contract and its processed product. Recognizing these relationships helps traders exploit price discrepancies and manage risk effectively.
Benefits of Futures Spread Trading
Low-Risk Strategy
Cryptocurrency markets are extremely volatile and in order to prevent such volatility and limit the risks, the trader will usually put a limit stop-loss position, which will be visible in the order book and will make him the perfect target for the large market player. Applying spread trading to the crypto futures will automatically reduce the overall volatility and at the same time will limit your risks in the event of the unpredictable market crashes.
Clear Investment Opportunities
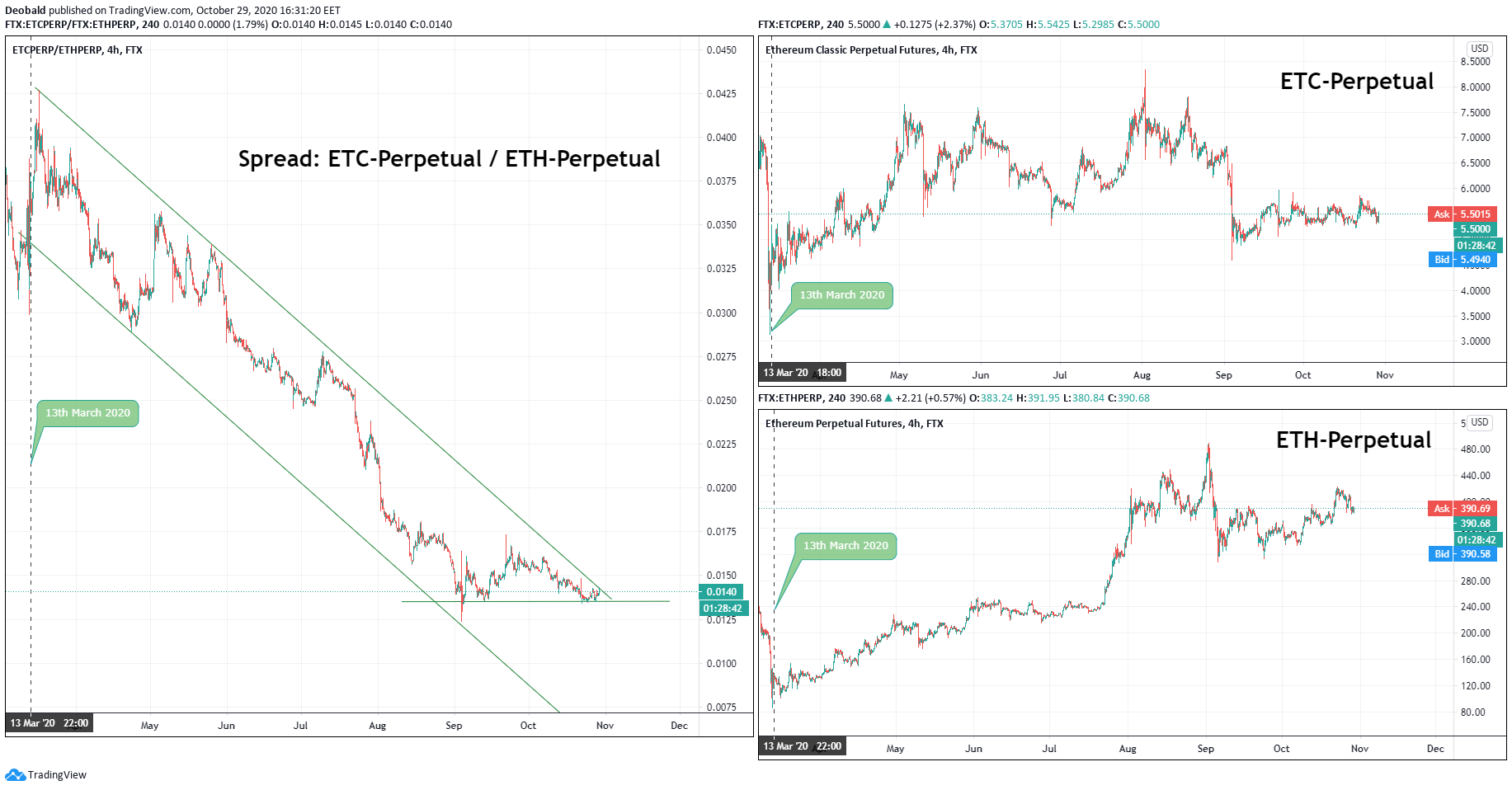
In most cases, crypto spreads typically trends more often in relation to the stand-alone futures. These trends are steeper and last longer.
Diversification of Strategies
Using spread trading in the highly correlated cryptocurrency markets will allow you to diversify your trading strategies. Based on the low risk in comparison to trading on futures along, the trader will have an option of implementing higher leverage or more volume in a single trade
High-risk trading on futures with low leverage can be substituted for the less risky option of spread trading with high leverage.
How to Trade Futures Spread in Crypto Markets
To start trading spreads on crypto futures, you need a crypto exchange account that allows trading crypto futures and a TradingView account to see the chart.
In order to understand how spread trading works in practice, let’s look at the example of ETH-PERP / BTC-PERP on FTX exchange. Spread trading typically involves taking both a long or short position and short positions at the same time, allowing you to profit from price discrepancies between two contracts.
First, let’s look at a chart. Go to TradingView chart and to get the spread of ETH-PERP / BTC-PERP on FTX exchange type:
FTX:ETHPERP/FTX:BTCPERP
You will see a chart showing a spread price. When selecting contracts for your spread, it is important to choose contracts with the same contract month for certain strategies to ensure accurate comparison and execution.
After you set the Take Profit and Stop Loss prices you are ready to trade.
You can now open FTX exchange and first, open the ETH-PERP in one window and open BTC-PERP in the other window. Once the price is acceptable to enter a position, make market orders on each asset. As a result, once you enter, you should have 2 futures positions open—one long and one short. Opening an offsetting position helps balance risk and manage margin requirements in your spread trade.
To exit the spread, close both of your positions simultaneously. Managing open futures positions requires you to monitor liquidity to ensure you can enter and exit trades smoothly without excessive slippage. The profitability of a spread trade depends on the relative performance of the contracts involved, and success often comes when a trader believes in a specific price movement between the two contracts.
Trading Tool for Crypto Futures Spread Trading
To decrease risks of spread trading on crypto even further we have created a special trading terminal.
Spread trading terminal allows you to select which assets you would like to use for creating a spread. The tool supports spread trading in various asset classes, including commodities like natural gas, heating oil, and soybean oil. To change the terminal view from Classic Trading to Spread Trading simply change the strategy type. You can find it right after the exchange selection dropdown.
It is available on all cryptocurrency exchanges that offer futures trading, currently, the list includes FTX, Deribit, Bybit and Binance Futures.
TradingView chart will instantly adapt and show you the synthetic product on the chart. Our Terminal will show what spread you’ve created in a simple way. The terminal can also be used for strategies such as the soybean crush, which involves trading both the raw commodity and its processed products.
What’s cool, you can then automate the trading and select Take Profit and Stop Loss targets as if you are trading a simple pair on the exchange. Targets will be monitored by Wunderbit and executed once the aim is reached.
Both entries and exits are done with a market order making sure you get the price you expected. On the one hand, limit entries are cheaper and make the spread trading more flexible. On the other hand, risks increase as price volatility on crypto markets is highly significant.
The platform is designed for spread trading futures across multiple markets.
Try futures spread trading on WunderTrading now!